K�a$�Y�KY,
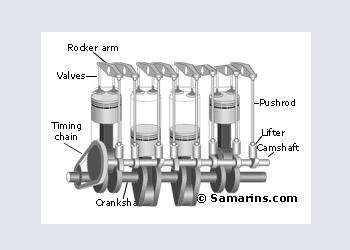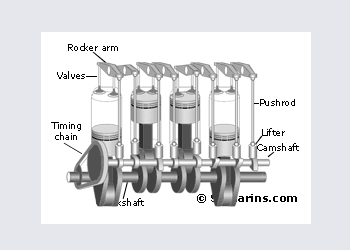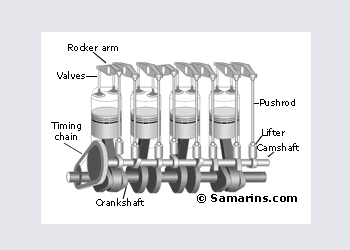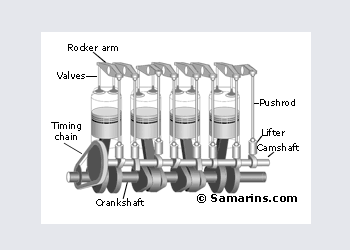
OHV engine design
OHV means OverHead Valve - an engine design where the camshaft is installed inside the engine block and valves are operated through lifters, pushrods and rocker arms (an OHV engine also known as "Pushrod" engine). Although an OHV design is a bit outdated, it has been successfully used for decades. An OHV engine is very simple, has more compact size and proven to be durable.
Downsides: it\'s difficult to precisely control the valve timing at high rpm due to higher inertia caused by larger amount of valve train components (lifter-pushrod-rocker arm). Also it\'s very difficult to install more than 2 valves per cylinder or implement some latest technologies such as Variable Valve Timing - something that could be easily done in a DOHC engine.
OHC or SOHC engine——我们的4G18就是类似这结构,不过是16气门,每缸4气门
OHC in general means OverHead Cam while SOHC means Single OverHead Cam.
In the SOHC engine the camshaft is installed in the cylinder head and valves are operated either by the rocker arms or directly through the lifters (as in the picture).
The advantage is that valves are operated almost directly by the camshaft - easy to achieve the perfect timing at high rpm. Also it\'s possible to install three or four valves per cylinder
The disadvantage - an OHC engine requires a timing belt or chain with related components - more complex and more expensive design.
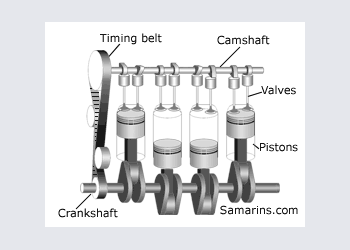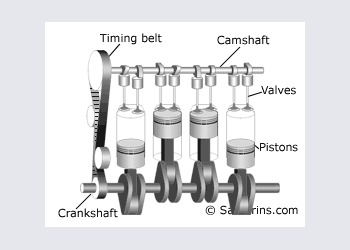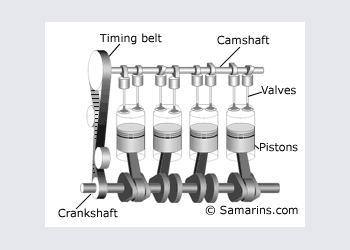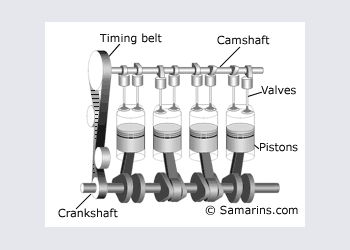
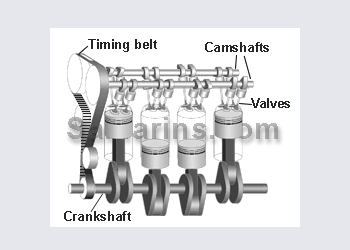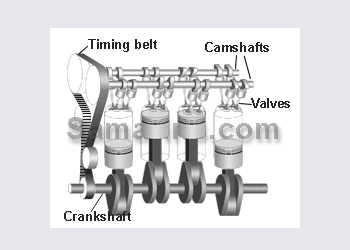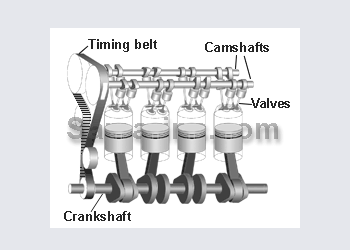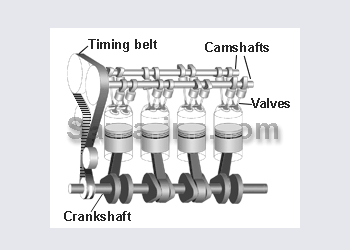
DOHC or Twin cam engine
DOHC or Double OverHead Cam - the setup used in many today\'s cars. Since it\'s possible to install multiple valves per cylinder and place intake valves on the opposite side from exhaust vales, DOHC engine can "breath" better meaning that it can produce more horsepowers with smaller engine volume. Compare: The 3.5-liter V6 DOHC engine of 2003 Nissan Pathfinder has 240 h.p, similar to 245 h.p of the 5.9-liter V8 OHV engine of 2003 Dodge Durango.
Pros: High efficiency, possible to install multiple valves per cylinder and adopt variable timing.
Cons: More complex and more expensive design.